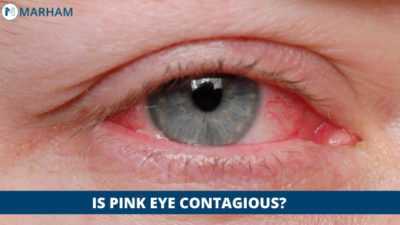
Conjunctivitis, commonly known as pink eye, is an inflammation of the conjunctiva, the transparent membrane lining the eyelid and eyeball. This condition causes the whites of the eyes to appear reddish or pink due to swollen blood vessels. While often resulting from a viral infection, it can also stem from bacterial infections, allergic reactions, or an incompletely opened tear duct, especially in babies.
Book an appointment right now to discuss your eye issue in detail.
The infection is particularly important in places with unhygienic living conditions. The number of people affected with pink or red eye infections in Karachi has suddenly risen. The surge is particularly linked to the rainy season and the associated increase in microorganisms.
How does Pink Eye infection Spread?
Pink eye infection can occur due to an infection or a foreign particle invading the eyes. The most common causes of conjunctivitis are:
Viral and Bacterial Conjunctivitis: Commonly caused by adenovirus and other viruses, they are contagious eye infections and often accompany respiratory infections. The infection can also occur due to bacterial invasion, such as improper contact lens use, leading to bacterial conjunctivitis.
Allergic Conjunctivitis: A reaction to allergens can cause symptoms like itching and tearing. This optical infection is not contagious and is typically treated with allergy eye drops.
Conjunctivitis from Irritation: It is caused by chemical splashes or foreign objects. The symptoms usually resolve in a day, but some chemicals or injuries may require medical attention.
Is Pink Eye Contagious?
Pink eye due to bacteria or viruses is highly contagious, while allergic conjunctivitis is not. The incubation period for viral or bacterial conjunctivitis is approximately 24 to 72 hours. Pink eyes can develop if you touch something with the virus or bacteria and then touch your eyes. Most bacteria can live on a surface for up to eight hours, but some can live for several days. Most viruses can survive on a surface for a few days, with some lasting up to two months.
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Pink Eye?
The first indication of pink eye is a change in the colour of your eye’s white part, known as the sclera. This tough outer layer protects the iris and the rest of the eye. The conjunctiva is a thin, transparent membrane covering the sclera and inflamed when you have pink eye.
The blood vessels in this eye infection get inflamed, making them more visible, and this causes your eye to appear red or pink. Pink eye is not always caused by inflammation or irritation of the conjunctiva. A closed tear duct may irritate the eye in infants. Swimming in a pool with lots of chlorine can also cause redness in your eyes.
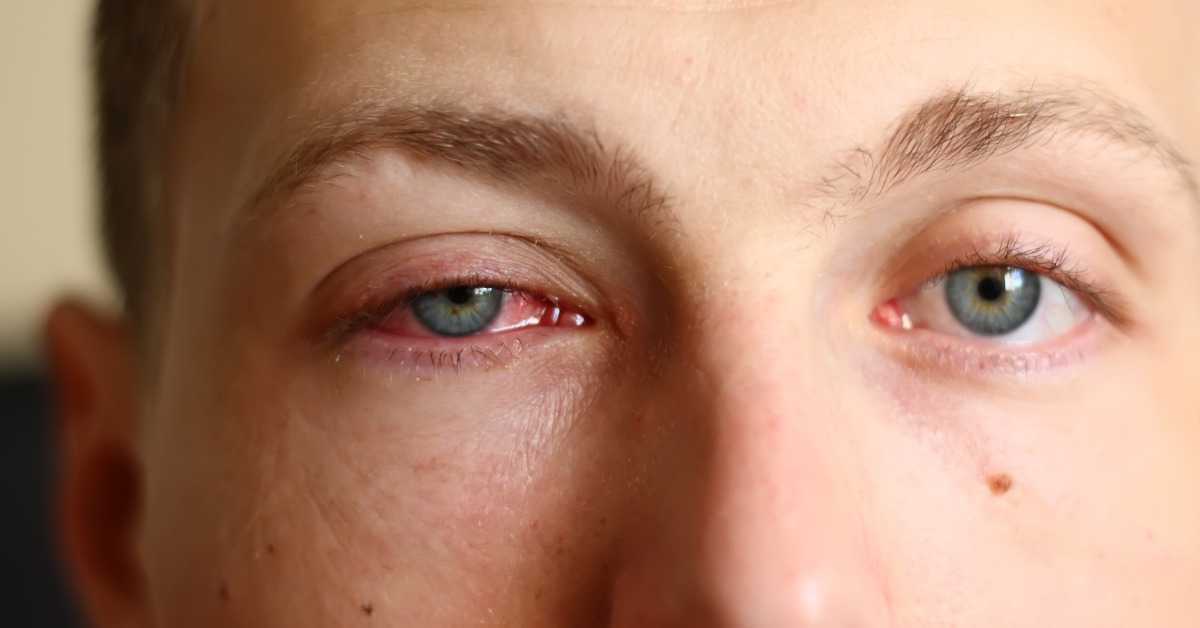
- Itchiness
- Gooey discharge that may form a crust around your eyelids while you sleep
- A feeling like dirt or something is irritating your eye
- Watery eyes
- Susceptibility to bright lights
Pink eyes can appear in either one or both eyes. If you wear contact lenses, they may feel very uncomfortable, as if they don’t fit properly. If at all possible, avoid wearing your contacts while experiencing symptoms. Conjunctivitis can cause swelling in the lymph node near your ear in severe cases. It may appear to be a small lump. The lymph nodes assist the body in fighting infections. The lymph node should shrink once the viral or bacterial infection has cleared.
How is Pink Eye identified?
Consult a doctor if you notice conjunctivitis symptoms in your or your child’s eyes. Early detection can help reduce symptoms and the risk of infection spreading to others.
The physical presentation of the signs and symptoms usually diagnoses conjunctivitis. The diagnostic methods include;
- Physical evaluation of eye redness or swelling
- Taking the patient’s medical history of any medicines or diseases the patient has.
- A lab test is usually performed on the eye discharge to diagnose bacterial, viral, or allergic conjunctivitis.
What is the Treatment for Pink Eye?
The treatment of pink eyes depends on the cause of the infection.
Bacterial Conjunctivitis Treatment:
Most bacterial conjunctivitis requires antibiotic eye drops or ointments to clear the infection.
Do not wear contact lenses until the infection has cleared.
- If you’ve worn soft contacts before the infection, it’s advisable to discard them. Disinfect hard lenses overnight before reusing them.
- Consider replacing your contact lens accessories, such as the lens case used before or during the illness.
- Replace any eye makeup used before the onset of the infection.
Viral Conjunctivitis Treatment:
Most viral conjunctivitis is self-limiting, meaning it will clear up in about 2 to 3 weeks.
- Artificial tears and cold or warm compresses can help alleviate symptoms.
- Avoid wearing contact lenses until the infection has cleared. For soft lenses worn before the infection, it’s recommended to discard them. For hard lenses, disinfect them overnight before reusing them.
- Antiviral medicines might be prescribed if the cause is the herpes simplex virus.
Allergic Conjunctivitis Treatment:
Avoid exposure to allergens that trigger the symptoms. Prescription or over-the-counter eye drops can help, including antihistamines, mast cell stabilizers, decongestants, steroids, and anti-inflammatory drops.
Seek advice from your ophthalmologist to determine the best treatment for your allergy symptoms.
How to Avoid Pink Eye?
Conjunctivitis eye infection can affect anybody at any age. However, a few preventive measures can help protect your eyes. These include;
- Keep your hands clean and avoid rubbing your eyes in case of itching or redness.
- Avoid close contact with anybody who is affected by the disease.
- Wipe the discharge from the eyes with a clean napkin or cloth and avoid contact with it.
- If your eyes have become sensitive, stop wearing the contact lens.
- Avoid sharing stuff like towels, pillows, or eye drops with anyone
Conclusion
The viral and bacterial pink eye is contagious, while the conjunctivitis caused by allergies is not contagious. You can reduce the risk of spreading the infection by taking preventive measures and avoiding contact with the public until the eye infection heals.
Book an appointment with the top eye specialists to discuss your symptoms or the risks of infection.
FAQs
1. Which eye drops are best for conjunctivitis?
Antibacterial and antiviral eye drops are suitable for treating conjunctivitis, depending on the cause of the infections. They include polymyxin, ciprofloxacin, and levofloxacin.
2. Do you need to stay home if you have pink eye?
Pink eye, both viral and bacterial, is highly contagious. Pink eye can affect adults and children therefore, avoid public places and contact with the people if you are suffering from the disease.
3. What gets rid of pink eye fast?
If you have bacterial pink eye symptoms, the best way to treat them is to see your doctor as soon as possible. Antibiotic eye drops will be prescribed by your doctor.