Your blood report shows dozens of values, but one small number (MCH) tells a surprisingly big story about your health. Understanding MCH meaning in blood test results can help you take charge of your health. If your doctor has flagged your MCH levels as abnormal, you’re probably wondering what it means and if you should be concerned.
Let’s break down everything about the MCH blood test.
What is MCH in Blood Test?
MCH stands for Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin. In Urdu, it’s called خون کے سرخ خلیوں میں ہیموگلوبن کی اوسط مقدار.
MCH measures the average amount of hemoglobin inside each of your red blood cells. Hemoglobin is the protein that carries oxygen from your lungs to every part of your body.
According to the Cleveland Clinic, MCH is measured in picograms (pg), a picogram is one-trillionth of a gram. This measurement helps doctors understand if your red blood cells are carrying the right amount of oxygen-transporting hemoglobin.
Key Point: MCH was first introduced by Dr. Maxwell Wintrobe in 1929 and has been a standard diagnostic tool for anemia ever since (NCBI).
MCH Blood Test Normal Range
The normal MCH range for adults is 27 to 33 picograms per cell (pg/cell), as per Cleveland Clinic. However, slight variations exist across laboratories:
| Age Group | Normal MCH Range |
| Adults (all ages) | 27-33 pg/cell |
| Children | 27-31 pg/cell |
| Newborns | 32-34 pg/cell |
Important: A value below 27 pg is considered low MCH, while a value above 33 pg is considered high MCH.
MCH Blood Test Low Causes
When your MCH is below the normal range, it means your red blood cells contain less hemoglobin than they should. This condition is associated with:
1. Iron Deficiency Anemia (Most Common)
This is the leading cause of low MCH worldwide. Without enough iron, your body can’t produce adequate hemoglobin. Common causes of iron deficiency include:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding
- Internal bleeding (ulcers, hemorrhoids)
- Poor dietary iron intake
- Malabsorption conditions (celiac disease, Crohn’s disease)
2. Thalassemia
A genetic blood disorder where the body produces less hemoglobin than normal. Thalassemia is particularly common in people of Mediterranean, South Asian, and Middle Eastern descent.
3. Chronic Disease-Related Anemia
Long-term conditions like kidney disease, liver disease, cancer, and autoimmune disorders can cause chronic inflammation that interferes with hemoglobin production.
4. Sideroblastic Anemia
A bone marrow disorder that prevents the body from properly using iron to make hemoglobin.
5. Lead Poisoning
Lead interferes with hemoglobin production and can damage bone marrow, leading to low MCH levels.
Symptoms of Low MCH
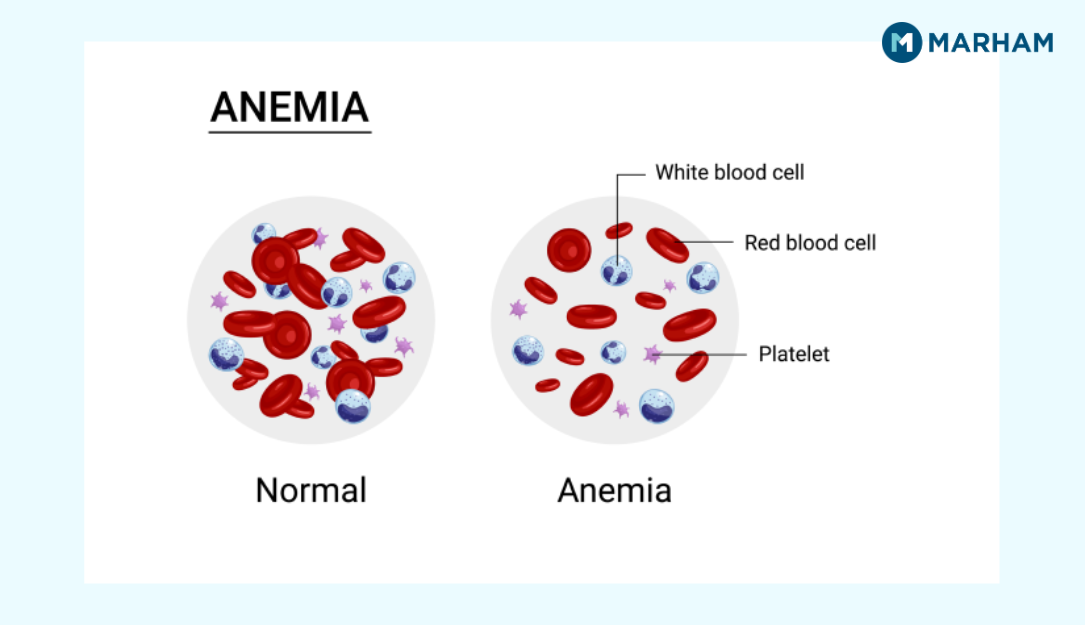
Low MCH presents with symptoms of anemia:
- Persistent fatigue and weakness
- Pale skin (especially noticeable on palms and nail beds)
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity
- Dizziness
- Lightheadedness
- Cold hands and feet
- Brittle nails
- Headaches
MCH Blood Test High Causes
A high MCH value means your red blood cells are larger than normal and contain more hemoglobin per cell. This is typically associated with macrocytic anemia.
1. Vitamin B12 Deficiency
B12 is essential for red blood cell production. Without it, your body produces abnormally large red blood cells. Sources of B12 include meat, fish, eggs, and dairy products.
2. Folate (Vitamin B9) Deficiency
Like B12, folate is crucial for healthy red blood cell formation. Deficiency is common in people with poor dietary intake or malabsorption issues.
3. Liver Disease
The liver plays a role in red blood cell metabolism. Liver dysfunction can lead to elevated MCH levels.
4. Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid)
Thyroid hormones affect red blood cell production. Low thyroid function can cause macrocytic anemia.
5. Chronic Alcohol Use
Long-term alcohol consumption damages the bone marrow and interferes with nutrient absorption, particularly folate and B12.
6. Certain Medications
Chemotherapy drugs, anticonvulsants, and some antibiotics can also elevate MCH levels.
Symptoms of High MCH
High MCH itself may not cause symptoms, but the underlying conditions can cause:
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Numbness or tingling in hands and feet (especially with B12 deficiency)
- Memory problems
- Confusion
- Mood changes
- Jaundice (yellowing of skin, if liver-related)
- Rapid heartbeat
How is MCH Tested?

MCH is not measured directly. It’s calculated as part of a Complete Blood Count (CBC), the most common blood test ordered by doctors.
The formula used is: MCH = Hemoglobin (g/dL) ÷ Red Blood Cell Count (million/µL) × 10
Your doctor may order additional tests based on your MCH results, including:
- Serum iron and ferritin levels
- Vitamin B12 and folate levels
- Thyroid function tests
- Liver function tests
Treatment for Abnormal MCH Levels
Treatment depends on the underlying cause:
For Low MCH:
- Iron supplements (oral or IV) for iron deficiency
- Dietary changes include taking iron-rich foods like red meat, spinach, lentils
- Blood transfusions for severe cases
For High MCH:
- Vitamin B12 supplements or injections
- Folic acid supplements
- Treating underlying conditions (thyroid, liver disease)
Consult a Hematologist at Marham!
Abnormal MCH levels should not be ignored. At Marham, we make it easy to get expert help. Connect with the best hematologists across Pakistan who can accurately diagnose the cause, guide you through the right tests, and create a personalized treatment plan
Call 0311-1222398 to book your online or physical consultation. You can also visit Marham.pk to find a trusted hematologist near you.
Your health matters. Get clarity. Get treated. Get better with Marham.
Frequently Asked Questions About MCH Blood Test
What does MCH blood test meaning in Urdu?
ایم سی ایچ کا مطلب ہر سرخ خون کے خلیے میں موجود ہیموگلوبن کی اوسط مقدار ہے، یہ قدر خون کے ٹیسٹ میں دیکھی جاتی ہے اور اس سے یہ اندازہ ہوتا ہے کہ سرخ خون کے خلیوں میں ہیموگلوبن مناسب مقدار میں موجود ہے یا نہیں، اور اگر یہ مقدار کم ہو تو عام طور پر یہ خون کی کمی کی طرف اشارہ کرتی ہے۔
What is the MCH full form in blood test?
MCH stands for Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin, the average hemoglobin per red blood cell.
Is low MCH serious?
Low MCH can indicate iron deficiency anemia. Although it is treatable, untreated cases can lead to heart complications. Consult a doctor for diagnosis.
Can I increase my MCH naturally?
For iron-deficiency-related low MCH, eating iron-rich foods with vitamin C can help. Always consult a doctor first.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment.

