Cervical cancer is a serious health problem in Pakistan. Every year, around 5,000 women are diagnosed with this disease, and about 3,200 women lose their lives because of it. It is the third most common cancer in Pakistani women and the second most common in women between the ages of 15 and 44. This shows how important it is to pay attention to this disease and take steps to prevent it.
In this blog, we will discuss what cervical cancer is, its sympto
ms, causes, and how timely vaccination can protect women. With the recent rollout of the HPV vaccine in Pakistan and increasing awareness, now is the right time to understand the facts and take action.
What is Cervical Cancer? (سرطانی خلیہ گردن / گردن کا کینسر)
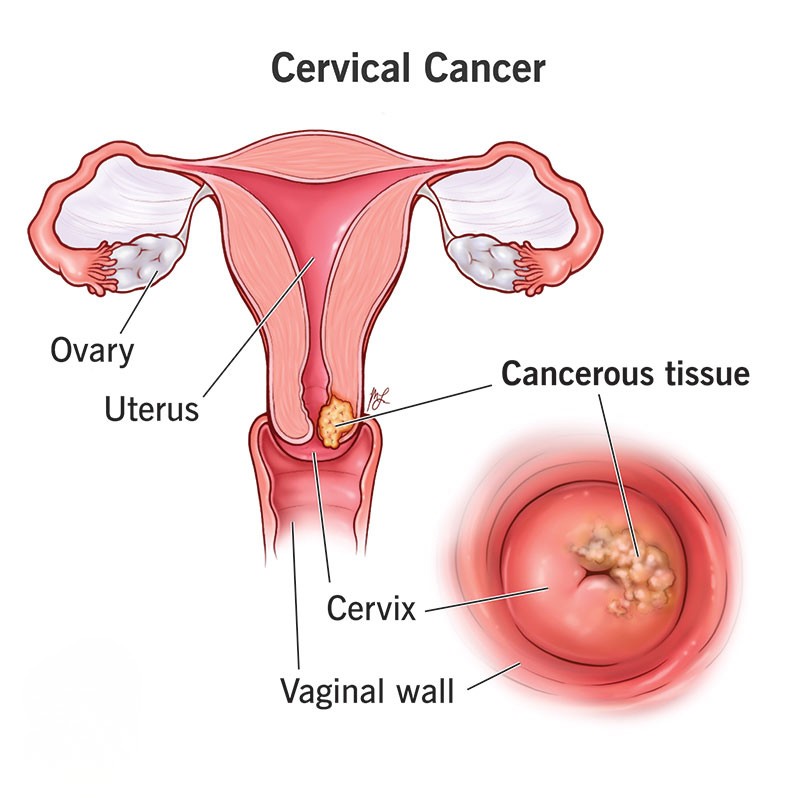
Image Source: Cleveland Clinic
It is a type of cancer that develops in the cervix, the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. It usually starts with abnormal cell changes. Over time, these cells can multiply and spread to other parts of the body.
Cervical cancer usually develops from long-lasting infections with certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV). Two types, HPV 16 and 18, are responsible for about 88% of severe cases.
Cervical Cancer Meaning in Urdu:
سروائیکل کینسر کا مطلب ہے رحم کی نالی یا بچہ دانی کے منہ (سروکس) میں پیدا ہونے والا کینسر۔ یہ خواتین میں پایا جانے والا ایک عام کینسر ہے جو زیادہ تر ایچ پی وی وائرس کے انفیکشن کی وجہ سے ہوتا ہے۔
Simply put, cervical cancer is when normal cells in the cervix start growing uncontrollably. This turns them into cancerous cells that may spread if not treated in time.
Cervical Cancer in Pakistan | Why Thousands of Women Are at Risk
Cervical cancer is a serious health issue in Pakistan. The number of women affected is higher than the target set by the World Health Organization (WHO) for eliminating this disease. This makes Pakistan one of the top 10 countries in the world with the highest death rate from cervical cancer.
A major reason behind this is the human papillomavirus (HPV), especially types 16 and 18. Around 0.5% of women in Pakistan carry these high-risk types of HPV, which cause almost 88% of cervical cancer cases in the country.
According to the Pakistan National Cancer Registry, nearly 6,000 new cases are reported every year. Other studies also show around 5,000 to 5,500 cases. Sadly, the death rate remains very high at about 60% since many women are diagnosed late and do not receive proper treatment on time.
Cervical Cancer Causes
The primary cause of cervical cancer is persistent infection with high-risk types (HPV 16 and 18) of HPV. Other risk factors include:
- Early sexual activity or multiple sexual partners
- Weakened immune system (e.g., HIV/AIDS)
- Smoking
- Long-term use of oral contraceptives
- Lack of regular screening and medical check-ups
Cervical Cancer Symptoms & Warning Signs
The symptoms of cervical cancer may not appear in its early stages. As it progresses, they can include:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding (between periods, after intercourse, or post-menopause)
- Unusual vaginal discharge (watery, bloody, or foul-smelling)
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Pelvic or lower back pain
- Unexplained weight loss and fatigue
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s best to talk to a gynecologist without delay. You can easily connect with a specialist through Marham and get the guidance you need.
Cervical Cancer Stages
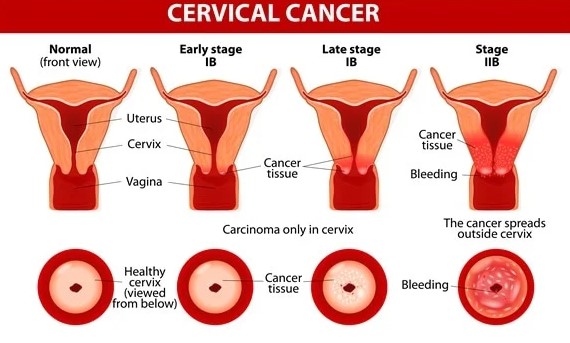
Image Source: News Medical
Doctors classify cervical cancer into four main stages. Each stage indicates how far the cancer has spread:
-
Stage 0 (Carcinoma in situ)
In stage 0, abnormal cells are present only on the surface of the cervix. It is highly treatable and curable.
-
Stage I
At this stage, cancer remains confined to the cervix. Women may notice minor bleeding or unusual discharge. Doctors can treat it effectively with surgery alone.
-
Stage II
Stage II is when cancer extends beyond the cervix but has not reached the pelvic wall. Its treatment usually involves surgery and radiation, sometimes combined with chemotherapy.
-
Stage III
At stage III, cancer spreads to the lower part of the vagina or pelvic wall. This possibly causes urinary or bowel problems. Radiation combined with chemotherapy is required to treat it.
-
Stage IV
In stage IV, cancer reaches nearby organs like the bladder or distant sites like lungs or liver. Its treatment focuses on chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and palliative care to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Cervical Cancer Risk Factors
Women are at higher risk if they:
- Have a persistent HPV infection
- Smoke or use tobacco
- Have a weakened immune system
- Have multiple sexual partners or early sexual activity
- Lack regular screenings like Pap smear tests
Cervical Cancer Diagnosis:
Doctors use several tests to detect cervical cancer early and determine its stage:
- Pap smear test: This simple test identifies abnormal cells in the cervix before they turn cancerous.
- HPV DNA test: It detects high-risk types of HPV that can cause cervical cancer.
- Colposcopy: It allows doctors to examine the cervix closely for any suspicious areas.
- Biopsy: This test confirms the presence of cancer and helps determine its stage.
Cervical Cancer Treatment:
The treatment of cervical cancer depends on the stage at which it is diagnosed. Early detection makes treatment easier, less invasive, and increases the chances of recovery. Doctors may recommend one or more of the following methods depending on the patient’s condition:
-
Surgery
Surgery is one of the most common treatments for cervical cancer, especially in the early stages. The goal is to remove the cancerous tissue, and in some cases, the uterus may also be removed (hysterectomy). When the cancer is detected early, surgery provides a very high chance of complete cure.
-
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses strong, high-energy rays to destroy cancer cells and shrink tumors. Doctors recommend it when the cancer has spread beyond the cervix but is still within the pelvic area. Sometimes, radiation is given after surgery to reduce the risk of the cancer coming back.
-
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves medicines that travel through the bloodstream to target cancer cells in the whole body. This treatment is usually given when cancer has spread to other parts of the body or alongside radiation to make it more effective. It helps slow the growth of cancer cells or destroy them completely.
-
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy focuses on specific changes in cancer cells that help them grow and survive. By attacking these specific molecules, targeted therapy can stop the cancer from spreading while causing less harm to normal, healthy cells. This option is usually used when other treatments are not enough on their own.
-
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy helps the body’s own immune system recognize and fight cancer cells. This method is considered in advanced cases of cervical cancer where the disease has spread or returned. Immunotherapy can give the immune system the boost it needs to attack the cancer more effectively.
6 Ways to Prevent Cervical Cancer
You can prevent cervical cancer by taking the right steps at the right time. Since HPV infection is the main cause, prevention focuses on protecting yourself from the virus and detecting early changes in the cervix through screening.
In Pakistan, HPV vaccination has already been introduced in 2025, which is a major breakthrough in women’s health. You can read more about the HPV vaccine in Pakistan here. Below are some important preventive measures:
1. HPV Vaccination
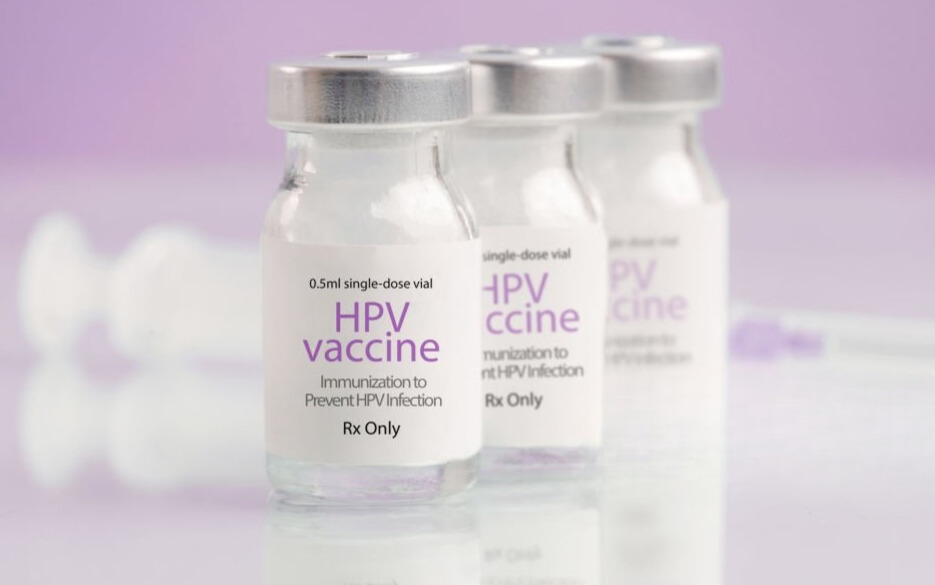
The HPV vaccine is the most effective way to prevent cervical cancer. Girls between 9–14 years should ideally get vaccinated before becoming sexually active. In Pakistan, the government has started rolling out the HPV vaccine. Women up to age 26 can also benefit if they haven’t been vaccinated earlier.
2. Regular Screening (Pap Smear & HPV Test)
Even vaccinated women should get Pap smear tests or HPV DNA tests as recommended by their doctor. Screening detects abnormal cells before they turn cancerous. With regular check-ups, you can stop the disease at the earliest stage.
3. Safe Sexual Practices
Using barrier protection like condoms lowers the risk of HPV transmission. Limiting the number of sexual partners and delaying sexual activity can also reduce exposure to high-risk HPV strains.
4. Quit Smoking
Smoking weakens the body’s ability to fight infections and makes cervical cells more vulnerable to cancer. Quitting tobacco can greatly reduce your risk.
5. Boost Immunity & Healthy Lifestyle
A strong immune system fights HPV naturally. To support cervical health, eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and vitamins, along with regular exercise.
6. Education & Awareness
It’s important to break myths and spread awareness about cervical cancer. In Pakistan, many women are unaware of the vaccine and screening options. Educating families and communities can increase vaccine acceptance and encourage women to go for early check-ups.
When to Consult a Doctor
If you notice any warning signs, like unusual bleeding, discharge, or pelvic pain, don’t wait. Seeing a gynecologist early can make a huge difference in treating cervical cancer successfully. You don’t even have to leave your home. With the Marham, you can:
- Find top gynecologists near you by specialty and location.
- Read doctor profiles, ratings, and reviews to choose the best fit.
- Book appointments online at a time that works for you.
- Consult doctors anytime, anywhere through video call.
Conclusion
Cervical cancer is a growing health concern in Pakistan, but it doesn’t have to be a death sentence. It is preventable and treatable if caught early. The HPV vaccine offers a safe, effective means to protect millions of Pakistani women.
Take control of your health today! Schedule a consultation with a gynecologist or oncologist in Pakistan through Marham. Protect yourself and encourage the women around you to get regular screenings.
Early action can save lives, and Marham makes it simple.

